2D Laminate Mechanics
Classical laminated Theory model for predicting effective elastic properties and ply level stresses and strains
Assumptions
- Each layer of the laminate is assumed to be both quasi homogeneous and orthotropic.
- The laminate is thin with its lateral dimensions is much larger than its thickness.
- The laminate is only loaded in the in-plane directions.
- All out of plane displacements are assumed to be small relative to the thickness of the laminate
- In-plane displacements vary linearly through the thickness of the laminate.
- All displacements are small compared with the thickness of the laminate.
- Normal distances from the middle surface remain constant.
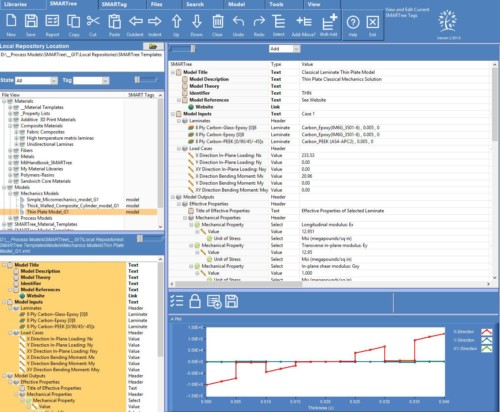
Model Inputs
- Laminate Definition (via laminate element)
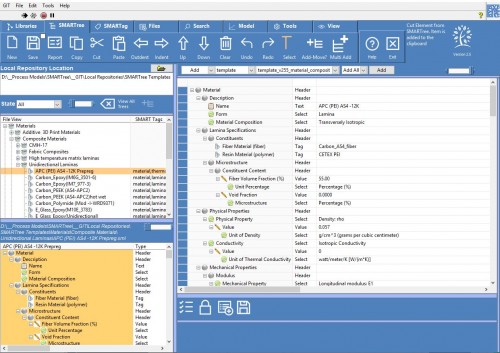
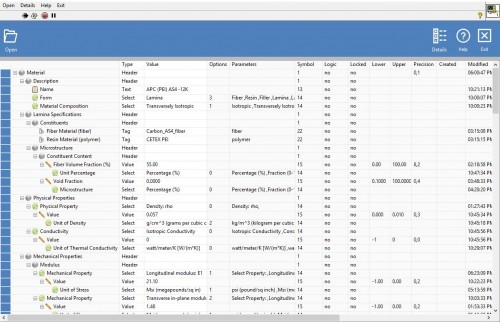
- Ply Material (via SMART Tag material, isotropic or orthotropic)
- Ply thickness (unit consistency with load required)
- Ply orientation (degrees)
- Delta temperature or moisture if included in analysis
- Laminate loading,
- In-plane loading: Nx, Ny, Nxy, (unit consistency)
- Bending moments: Mx, My, Mxy (unit consistency)
Model Outputs
- Effective Properties of Composite laminate including Ex, Ey, vxy, Gxy.
- ABD and abcd matrix.
- Effective displacements in-plane and bending
- Global and principle ply level stresses and strains